微语:代码适合中午敲,早晚出BUG
微语:代码适合中午敲,早晚出BUG
vue3写了一个路由标签导航栏组件 Vue
vue3里面引入就可以使用,vue2需要注册一下在调用。
大致思路,进入页面的时候监听路由,判断当前路由的地址,然后把这个地址用来做激活样式匹配,接下来就是点击事件,点击谁就把激活样式给谁,其次是删除如果删除的是第一个,下次跳转默认下标为0的标签,并且附带激活样式,如果不是就跳转上一个也是index+1。这里面用了一点ts语法!
<LabelNav />
<script lang="ts" setup>
import LabelNav from '../components/LabelNav.vue'
</script>效果展示:
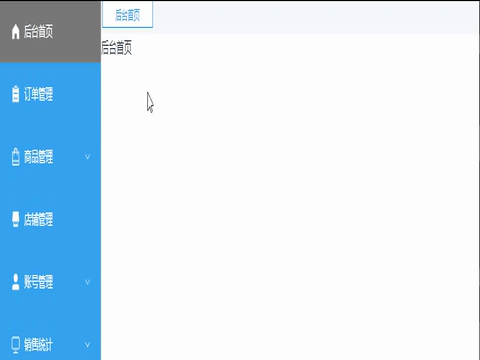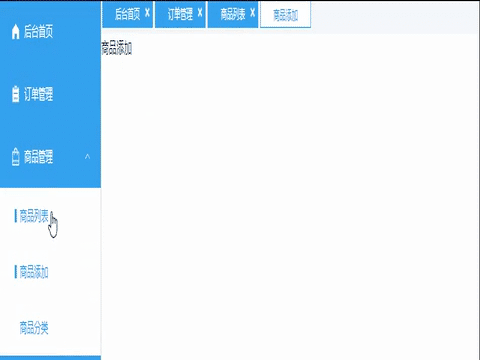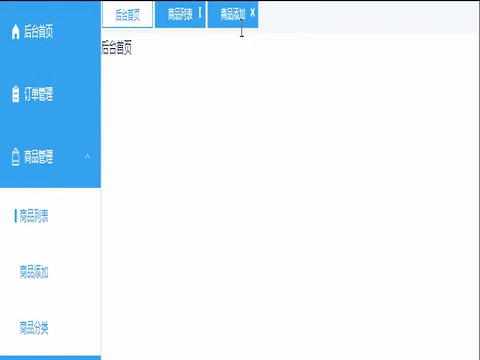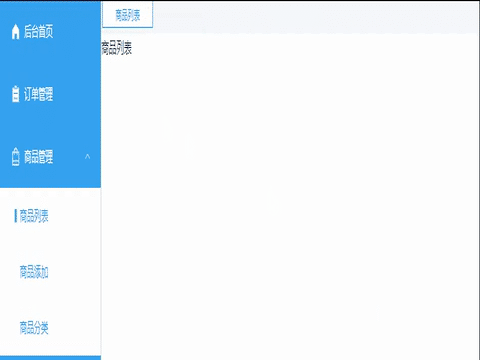
完整代码
<template>
<div class="DynamicMenu">
<el-scrollbar>
<div class="scrollbar-flex-content">
<div @click="switching(item.to)" :class="{ 'DynamicMenu-span': true, 'active': item.to == path }"
v-for="(item, index) in label " :key="index">
<span>{{ item.title }}</span>
<span @click="removeTag(index); $event.stopPropagation()" class="ax"></span>
</div>
</div>
</el-scrollbar>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { reactive, watch, ref } from 'vue';
import { useRoute, useRouter } from 'vue-router';
let $route = useRoute()
let $router = useRouter()
interface LabelItem {
title: string;
to: string;
}
let path = ref()
let label = reactive<LabelItem[]>([
])
path.value = $route.path
// 页面加载的时候读取本地tab标签
const storedTabs = localStorage.getItem('tab');
if (storedTabs) {
const newTabs = JSON.parse(storedTabs) as LabelItem[];
newTabs.forEach(newTab => {
const hasDuplicate = label.some(item => item.title === newTab.title);
if (!hasDuplicate) {
label.push(newTab);
}
});
} else {
label.push({ title: '后台首页', to: '/index' })
localStorage.setItem('tab', JSON.stringify(label))
}
// 监听路由变化,进行激活样式更改和标签存储
watch(() => $route.meta.title, (newTitle) => {
path.value = $route.path//激活样式
let tis: string = newTitle as string;
// 检查是否存在相同的项,存储标签
const hasDuplicate = label.some(item => item.title === tis);
if (!hasDuplicate) {
label.push({ title: tis, to: $route.path });
localStorage.setItem('tab', JSON.stringify(label))
}
});
// 删除标签
let removeTag = (index: number) => {
if (label.length === 1) {
return;
} else {
label.splice(index, 1);
// 如果删除的是第一个标签,则跳转下一个,反之则跳转上一个
if (index === 0) {
path.value = label[0].to;
$router.push(label[0].to);
} else {
path.value = label[index - 1].to;
$router.push(label[index - 1].to);
}
localStorage.setItem('tab', JSON.stringify(label));
}
}
// 点击标签跳转
let switching = (to: string) => {
path.value = to
$router.push(to)
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.DynamicMenu {
width: 100%;
height: 30px;
background-color: #f5f7fa;
position: relative;
top: 0;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
.DynamicMenu-span {
height: 25px;
min-width: 100px;
background-color: #35a2ef;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
margin: 0 2px;
padding: 0 10px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #fff;
position: relative;
span {
height: 100%;
line-height: 25px;
}
}
.ax {
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
position: relative;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
}
.DynamicMenu-span .ax::after,
.DynamicMenu-span .ax::before {
content: "";
width: 2px;
height: 10px;
top: 6px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: #fff;
right: 10px;
position: absolute;
transition: transform 0.3s ease;
}
.DynamicMenu-span .ax::after {
transform: rotate(-45deg);
}
.DynamicMenu-span .ax::before {
transform: rotate(45deg);
}
.DynamicMenu-span .ax:hover::after {
transform: rotate(45deg);
background-color: #ff0000;
}
.DynamicMenu-span .ax:hover::before {
transform: rotate(-45deg);
background-color: #ff0000;
}
.active {
background-color: white;
color: #35a2ef;
border: 1px solid #35a2ef;
}
}
.scrollbar-flex-content {
display: flex;
}
.scrollbar-demo-item {
flex-shrink: 0;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 4px;
background: var(--el-color-danger-light-9);
color: var(--el-color-danger);
}
</style>Vue中API接口如何二次封装Axios进行高效开发 Vue
1.src目录下新建 utlis文件夹 ->axios.ts
引入axios插件,创建公共服务器IP ,设置请求拦截器和相应拦截器,最后暴露出去
import axios from "axios"
export const SERVER_IP = 'http://XXXXXX/'
export const request = axios.create({
baseURL: SERVER_IP,
timeout: 6000,
})
//请求拦截器
request.interceptors.request.use()
//相应拦截器
request.interceptors.response.use()2.src目录下创建 apis文件夹->里面存储分类接口例如用户接口,登录接口:login.ts
引入封装的axios,进行接口的一个封装,然后暴露出去
import { SERVER_IP, request } from '../utlis/axios'
import type { Login } from './interface'
// 登录接口
export const $_checkLogin = (data: Login) => {
return request({
url: '/users/checkLogin',
method: 'POST',
data
})
}
//获取列表
export const $_UsersList = (params: userList) => {
return request({
url: '/users/list',
method: 'GET',
params
})
}3.在需要使用接口的页面只需调用封装的api也就是apis文件夹里面的文件例如:login.ts
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue';
import { $_checkLogin } from '../apis/login'
let form = reactive({
account: '',
password: ''
});
let onSubmit = () => {
$_checkLogin(form).then(res => {
//请求成功之后操作
})
}
</script>封装的好处方便我们后期维护管理API,如果吧api直接在写每个页面进行直接发请求,文件多起来了,就变的难以维护,如果用到了相同的请求也会造成代码冗余度过高。
封装之后对接口统一进行管理,更方便直观的查看API和维护,也降低了代码冗余度,和可读性。
以上示例都是基于Vue3+Ts写的,用Vue2+JS封装流程也是一样,只是不需要reactive这种响应式
vue3如何使用动态class切换 Vue
这里写的是一个旋转按钮使用的是elementPlus
vue3动态class三目预算:class="isRotated ? 'rotate' : 'reverseRotate'"通过点击事件给变量取反来实现class样切换
HTML
<div class="numE" @click="numE">
<el-icon ref="numElement" color="#fff" size="30px" :class="isRotated ? 'rotate' : 'reverseRotate'">
<Expand />
</el-icon>
</div>CSS
.rotate,
.reverseRotate {
transition: transform 0.5s ease;
}
.rotate {
transform: rotate(180deg);
}
.reverseRotate {
transform: rotate(0deg);
}JS
import { ref } from 'vue'
let isRotated = ref(false)
let numE = () => {
isRotated.value = !isRotated.value;
}vue3的动态css v-bind() Vue
vue3支持 css中支持v-bind来绑定动态样式值,例如:
<template>
<span>123</span>
</template><script setup>
let color="#fff"
</script><style lang="scss" scoped>
span {
background-color: black;
color: v-bind(color);
}
</style>Vue3的生命周期有哪些? Vue
DOM节点挂载前
onBeforeMount(() => {
console.log('DOM节点挂载前');
})DOM节点挂载后
onMounted(() => {
console.log('DOM节点挂载后');
})更新前
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
console.log('更新前');
})更新后
onUpdated(() => {
console.log('更新后');
})卸载前
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
console.log('卸载前');
})卸载完成后
onUnmounted(() => {
console.log('卸载完成后');
})点击元素让其滚动到锚点定位scrollIntoView方法 Vue
示例:
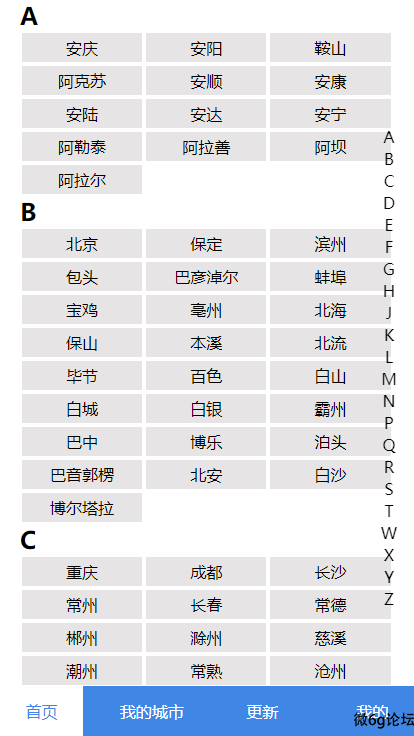
点击右侧的字母,滚动到具体的位置,先给右侧的标题绑定点击事件,拿到点击的元素,在通过scrollIntoView方法进行滚动
{ behavior: "smooth" }是平滑滚动属性
<div class="aside">
<ul>
<li @click="clickAZ(item)" v-for="(index, item) in abclist.list" :key="item">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="bscroll">
<ul class="index">
<li v-for="(index, item) in abclist.list" :key="item">
<h2 :id="item">{{ item }}</h2>
<div class="span">
<span :class="{ 'active': datalist.cityname == item }" @click="span(item)" v-for="(item, v) in index"
:key="v">
{{ item }}</span>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>JS
let clickAZ = (key) => {
console.log(key);
let element = document.getElementById(key);
element.scrollIntoView({ behavior: "smooth" });
}CSS
body,html{
height: 100%;
}
.bscroll {
height: 100%;
overflow: scroll;
}
.index{
height: 100%;
}Vue3如何使用vue-router进行跳转 Vue
1.首先配置路径信息,已经单独写过一篇了 点击前往
2.引入包文件
import { useRouter } from 'vue-router'3.定义变量接一下useRouter实例
let router = useRouter()4.使用router.push() 进行跳转()里面为path地址
router.push('/index')Vue3配置路由信息过程VueRouter Vue
1.引入包文件
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router';2.引入组件地址,也可以使用懒加载引入
import Home from '../views/Home.vue';//引入模式3.配置路由数组
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/info', component: () => import('../views/Info.vue') },
];4.创建路对象
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes,
});5.暴露出去
export default router6.在main.js中引入使用
const app = createApp(App) // 创建Vue应用程序实例,并传入根组件App
app.use(router)
app.mount('#app') // 将应用程序挂载到页面上的#app元素7.App.vue中放置出口
<router-view />完整示例:
ruoter.js
// 配置路由文件
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router';
import Home from '../views/Home.vue';
// 配置路由数组
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/info', component: () => import('../views/Info.vue') },
];
// 创建路由对象
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes,
});
// 暴露对象
export default routermain.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router/router'
const app = createApp(App) // 创建Vue应用程序实例,并传入根组件App
app.use(router)
app.mount('#app') // 将应用程序挂载到页面上的#app元素App.vue
<template>
<router-view />
</template>